Blacklisting is a crucial cybersecurity measure used to block access to harmful websites, protecting users from threats like malware and phishing.
This guide explores how websites can get blacklisted, the impact on businesses, and steps to recover and prevent blacklisting.
It includes practical advice on identifying issues, cleaning and securing your site, removing blacklist warnings, and maintaining ongoing security.
Let’s explore about What is a URL Blacklist?
About Google Blacklist: What is Blacklisting?
Blacklisting is a cybersecurity measure that blocks access to harmful websites. Search engines, antivirus companies, and security organizations ban sites that break their rules to protect users.
When a site is blacklisted, users see warnings to keep them safe from threats.
Google uses algorithms and user feedback to flag harmful sites, categorizing them as social engineering pages, malware pages, or unwanted software pages.
While this improves online safety, it can hurt businesses if their sites are compromised and blacklisted.
What is URL Blacklisting?
URL blacklisting is when search engines or security organizations block websites that break the rules.
This can lead to lower search rankings or complete removal from search results, making the website invisible to users online.
URL Blacklist in Google Chrome
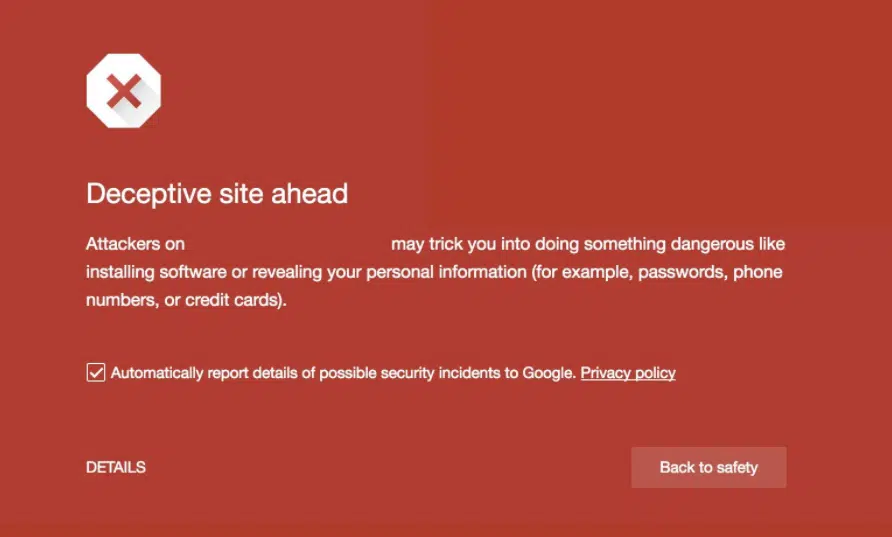
Understanding Google Chrome’s Warning Pages
When using Google Chrome, you might see warnings like “The site ahead contains malware” or “Deceptive site ahead” when trying to access certain websites. These warnings indicate that the site may contain malware or be a phishing site.
What do the Warnings Mean?
1. Malware Warning:
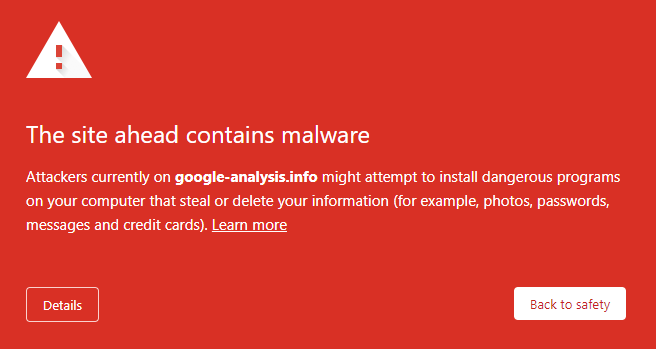
The site might have harmful software that can damage your computer.
2. Deceptive Site Warning:
The site may try to trick you into giving personal information or installing unwanted software.
User Choices
While you can choose to proceed to the site, most users return to the previous page to avoid potential risks. This warning system is a simple yet effective way to protect users from online threats.
Google’s Approach
Google uses algorithms and user feedback to identify and flag harmful sites. This process helps keep users safe but can impact businesses if their sites are flagged unintentionally.
Understanding these warnings and taking preventive steps can help avoid these issues.
The term “blacklisting” has been abandoned by Google since May 2018. The term “blocklisting” will now be used in the subsequent discussion in place of this one.
How a Website Can Get Blacklisted?
Websites can be banned for several reasons, mainly related to security issues or policy violations:
1. Malware Distribution: Sites that spread harmful software, intentionally or due to hacking, will be blacklisted to protect users.
2. Phishing Attempts: Sites trying to steal personal information like passwords or credit card numbers will be banned.
3. Spamming: Sites involved in sending spam emails or posting spammy content can be blacklisted.
4. Unwanted Content: Hosting content against platform policies, such as adult or violent content, can lead to a ban.
5. Unethical SEO Practices: Using black-hat SEO techniques like keyword stuffing or cloaking can get a site banned.
6. Shared Hosting Issues: If your site shares a server with blacklisted sites, it might also get banned.
7. Hacked Website: A hacked site used for malicious purposes can end up blacklisted.
How To Preven Blacklisting?
To avoid being blacklisted, follow website security best practices, adhere to SEO guidelines, ensure content compliance with platform policies, and regularly monitor for suspicious activity.
Determining if a Webpage is Blacklisted
- Google Search: Conduct a site query on Google (e.g., site.com). A warning message in the search results indicates potential blacklisting.
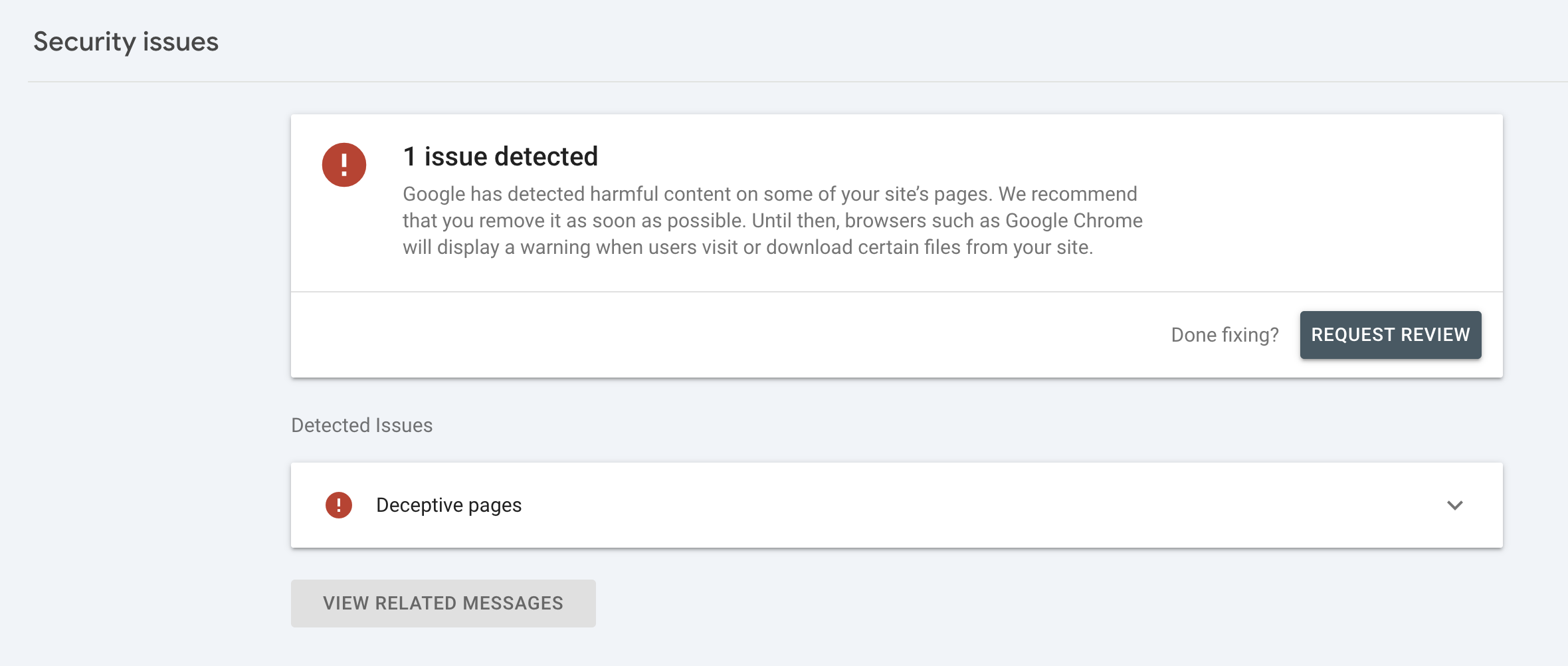
- Google Search Console: Use this tool for site analysis. Administrators receive direct notifications about security issues.
- Transparency Report: Google’s tool checks if a site is delisted due to copyright issues.
- Other Tools: Various free online tools can check if a domain is blacklisted.
About Reconsideration Request
If blacklisted, remove problematic content and resolve security issues, then submit a detailed reconsideration request to Google. Reindexing can take 1-5 days.
About Other Blacklists
Many organizations have blacklists for IPs and URLs spreading malware. Content Management Systems (CMS) can use custom blacklists for user content.
Email blacklists block spam senders, but different providers maintain separate lists.
Quick Links:
- How Do I Delete My Reviews On Google?
- How To Track And Analyze Traffic From A Google Business Profile To A Website?
- How Do I Delete My Reviews On Google?
- How To Delete Google Search History
Conclusion: Fix URL Blacklist
Understanding and addressing blacklisting is essential for maintaining your website’s visibility and trustworthiness.
By following best practices for security and compliance, you can protect your site from being blacklisted, ensure a safe experience for users, and recover effectively if your site is flagged.
Regular monitoring and proactive measures are key to preventing future issues.